Mar 4, 2022A particular reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 147 s when its initial concentration is 0.251 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 209 s when its initial concentration is 0.177 M. What formula do we use to solve for value of the rate constant for the reaction? Top Praveena Ratnavel – 1A Posts:101
OneClass: A reaction is first order in A. If the rate constant of the reaction is 3.45 times 10^-3 s^…
Jan 4, 202401/04/2024 Chemistry High School answer answered A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 155s when its initial concentration is 0.364. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 211s when its initial concentration is 0.267. a) TBD b) Pending calculations c) Insufficient data d) Results to come Advertisement

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
Mar 11, 2023Achieve Week 9-10 #12. Question #12 says “A particular reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 113 s when its initial concentration is 0.392 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 243 s when its initial concentration is 0.182 M. Determine the reaction order.” I’m just a little confused about how to determine the reaction order

Source Image: wyzant.com
Download Image
A review on hydrothermal carbonization of potential biomass wastes, characterization and environmental applications of hydrochar, and biorefinery perspectives of the process – ScienceDirect
Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 125 s when its initial concentration is 0.281 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 225 s when its initial concentration is 0.156 M. A) Determine the reaction order.

Source Image: askfilo.com
Download Image
A Particular Reactant Decomposes With A Half Life Of
Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 125 s when its initial concentration is 0.281 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 225 s when its initial concentration is 0.156 M. A) Determine the reaction order.
A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 107 s when its initial concentration is 0.349 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 239 s when its initial concentration is 0.156 M. Determine the reaction order. What is the value and unit of the rate constant for this reaction? Follow • 2 Add comment Report 1 Expert Answer
Q. 2. (i) Write the rate law for a first order reaction. Justify the stat..
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 137 s when its initial concentration is 0.380 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 243 s when its initial concentration is 0.214 M. Determine the reaction order. What is the value and unit of the rate constant for this reaction?
For a first order reaction 60% of the reactant decomposes in 45 minutes.a) Calculate the half life of the – Brainly.in

Source Image: brainly.in
Download Image
Problem 6.9 :In a first order reaction 60% of the reactant decomposes in ..
Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 137 s when its initial concentration is 0.380 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 243 s when its initial concentration is 0.214 M. Determine the reaction order. What is the value and unit of the rate constant for this reaction?
Source Image: askfilo.com
Download Image
OneClass: A reaction is first order in A. If the rate constant of the reaction is 3.45 times 10^-3 s^…
Mar 4, 2022A particular reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 147 s when its initial concentration is 0.251 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 209 s when its initial concentration is 0.177 M. What formula do we use to solve for value of the rate constant for the reaction? Top Praveena Ratnavel – 1A Posts:101

Source Image: oneclass.com
Download Image
A review on hydrothermal carbonization of potential biomass wastes, characterization and environmental applications of hydrochar, and biorefinery perspectives of the process – ScienceDirect
Mar 11, 2023Achieve Week 9-10 #12. Question #12 says “A particular reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 113 s when its initial concentration is 0.392 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half‑life of 243 s when its initial concentration is 0.182 M. Determine the reaction order.” I’m just a little confused about how to determine the reaction order

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
PPT – SAMPLE EXERCISE 14.1 Calculating an Average Rate of Reaction PowerPoint Presentation – ID:178913
Jan 30, 2023The half-lives of radioactive isotopes can be used to date objects. The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the reactant concentration to decrease to one-half its initial value. The half-life of a first-order reaction is a constant that is related to the rate constant for the reaction: t 1/2 = 0.693/ k.

Source Image: slideserve.com
Download Image
SOLVED: For a first-order reaction, the half-life is constant. It depends only on the rate constant k and not on the reactant concentration. It is expressed as t1/2 = 0.693/k. For a
Science Chemistry Chemistry questions and answers A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 125 s when its initial concentration is 0.281 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 225 s when its initial concentration is 0.156 M. A) Determine the reaction order.

Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Solved A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of | Chegg.com
A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 107 s when its initial concentration is 0.349 M. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 239 s when its initial concentration is 0.156 M. Determine the reaction order. What is the value and unit of the rate constant for this reaction? Follow • 2 Add comment Report 1 Expert Answer
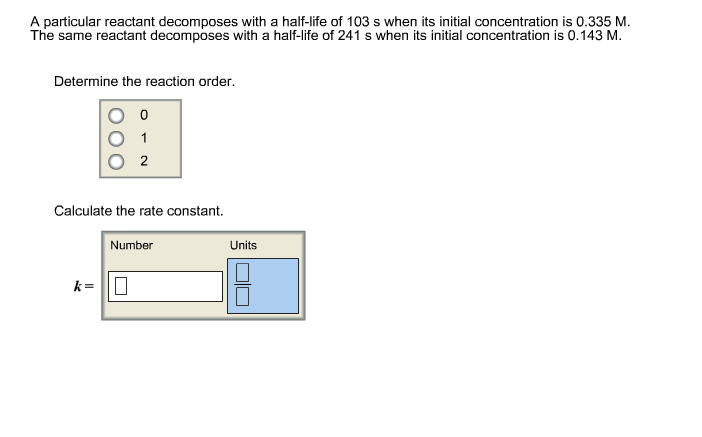
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Problem 6.9 :In a first order reaction 60% of the reactant decomposes in ..
Solved A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of | Chegg.com
Jan 4, 202401/04/2024 Chemistry High School answer answered A particular reactant decomposes with a half-life of 155s when its initial concentration is 0.364. The same reactant decomposes with a half-life of 211s when its initial concentration is 0.267. a) TBD b) Pending calculations c) Insufficient data d) Results to come Advertisement
A review on hydrothermal carbonization of potential biomass wastes, characterization and environmental applications of hydrochar, and biorefinery perspectives of the process – ScienceDirect SOLVED: For a first-order reaction, the half-life is constant. It depends only on the rate constant k and not on the reactant concentration. It is expressed as t1/2 = 0.693/k. For a
Jan 30, 2023The half-lives of radioactive isotopes can be used to date objects. The half-life of a reaction is the time required for the reactant concentration to decrease to one-half its initial value. The half-life of a first-order reaction is a constant that is related to the rate constant for the reaction: t 1/2 = 0.693/ k.