Jul 12, 2023The product formed when the bond to H is formed is called the conjugate acid. We can also draw the reverse of the previous reaction. Look at this carefully. we are still breaking a bond to H and forming a bond to H, but we’ve swapped everything. we are breaking N-H and C-Na, and forming N-Na and C-H. It’s still an acid-base reaction.
Draw the major organic product(s) of each of the following reaction (multiple products may be drawn if necessary): | Homework.Study.com
Expert Solution keyboard_arrow_down Interpretation Introduction (a) Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn. Concept introduction: The addition of an electrophile to an alkyne is followed by Markovnikoff’s rule and anti-stereoselectivity.
Source Image: ask.learncbse.in
Download Image
Chapter 13 / Lesson 1 32K Learn about the oxidation of alcohols. Understand oxidation of alcohols mechanisms, oxidation reagents, and see oxidation of propanol and cyclohexanol. Related to this
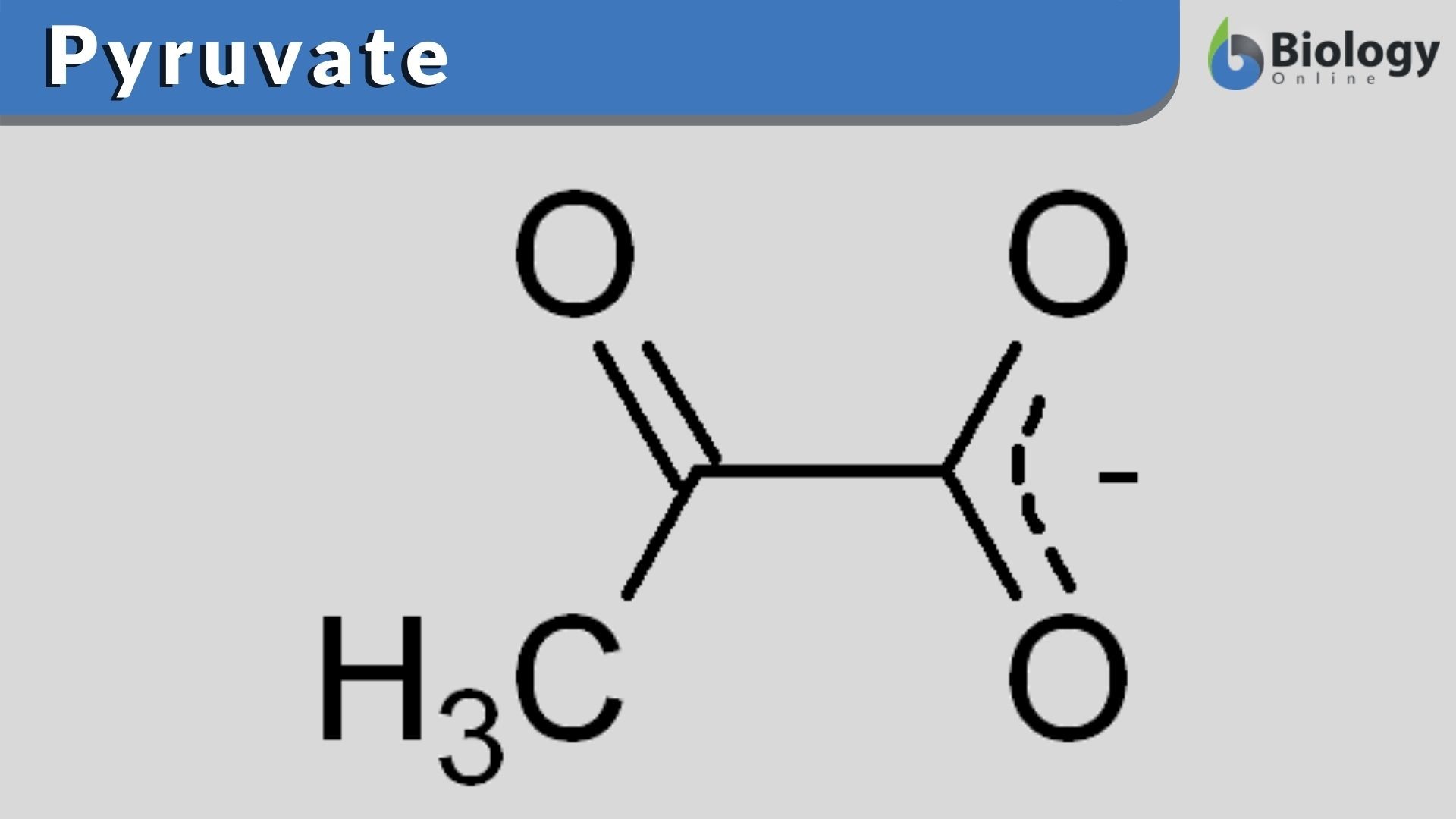
Source Image: biologyonline.com
Download Image
Asymmetric Aldol Reactions Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Draw organic products formed in the following reaction. Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login … The number of H atoms attached to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of organic products formed in the following reaction is: Medium. View solution > Draw organic products formed in the following

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Draw The Organic Product Formed In The Following Reaction
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Draw organic products formed in the following reaction. Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login … The number of H atoms attached to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of organic products formed in the following reaction is: Medium. View solution > Draw organic products formed in the following (a) Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn. Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors E2 mechanism to yield alkenes. The mechanism is concentrated and takes place in single step.
Draw a stepwise detailed mechanism that illustrates how four organic products are formed in the following reaction. | Homework.Study.com
Draw the organic molecule ( s) which is ( are) formed in the following reaction. Do not include molecules like H 2 O or H C l. ( You have 3 chances until the. Draw only one molecule in each drawing box. If need more compounds for your answer, click this button ADD DRAWING BOX. There are 2 steps to solve this one. Draw the major organic product formed in the following reaction. | Homework.Study.com

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Solved Click the “draw structure” button to launch the | Chegg.com Draw the organic molecule ( s) which is ( are) formed in the following reaction. Do not include molecules like H 2 O or H C l. ( You have 3 chances until the. Draw only one molecule in each drawing box. If need more compounds for your answer, click this button ADD DRAWING BOX. There are 2 steps to solve this one.
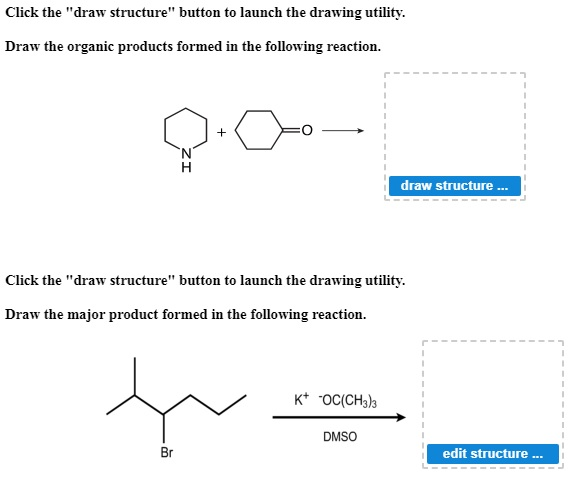
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Draw the major organic product(s) of each of the following reaction (multiple products may be drawn if necessary): | Homework.Study.com Jul 12, 2023The product formed when the bond to H is formed is called the conjugate acid. We can also draw the reverse of the previous reaction. Look at this carefully. we are still breaking a bond to H and forming a bond to H, but we’ve swapped everything. we are breaking N-H and C-Na, and forming N-Na and C-H. It’s still an acid-base reaction.

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Asymmetric Aldol Reactions Chapter 13 / Lesson 1 32K Learn about the oxidation of alcohols. Understand oxidation of alcohols mechanisms, oxidation reagents, and see oxidation of propanol and cyclohexanol. Related to this

Source Image: chem-is-you.blogspot.com
Download Image
Solved Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. | Chegg.com The organic product formed in given reaction is shown below. Figure 1. The above reaction takes place between a brominated compound and Li 2 CO 3, LiBr in the presence of DMF that results in the formation of an alkene as the desired product.
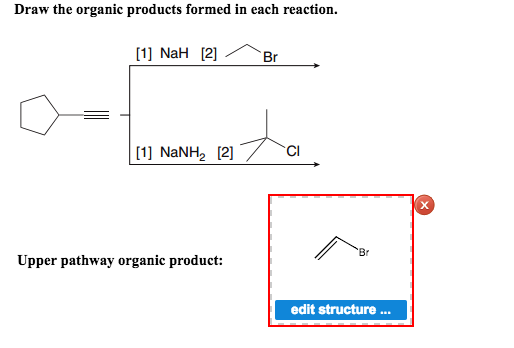
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Draw the major organic product(s) formed from the following reaction. | Homework.Study.com Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Draw organic products formed in the following reaction. Solve Study Textbooks. Join / Login … The number of H atoms attached to the carbon atom of the carbonyl group of organic products formed in the following reaction is: Medium. View solution > Draw organic products formed in the following

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
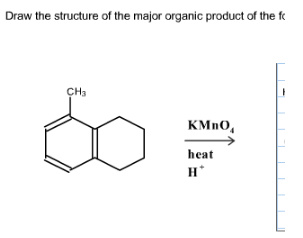
Draw the major organic product formed in the following reaction – Home Work Help – Learn CBSE Forum (a) Interpretation: The organic product formed in the given reaction is to be drawn. Concept introduction: The dehydrohalogenation reaction of primary alkyl halide mostly favors E2 mechanism to yield alkenes. The mechanism is concentrated and takes place in single step.
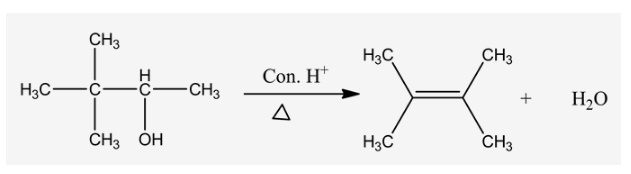
Source Image: ask.learncbse.in
Download Image
Solved Click the “draw structure” button to launch the | Chegg.com
Draw the major organic product formed in the following reaction – Home Work Help – Learn CBSE Forum Expert Solution keyboard_arrow_down Interpretation Introduction (a) Interpretation: The product that is formed by the reaction is to be drawn. Concept introduction: The addition of an electrophile to an alkyne is followed by Markovnikoff’s rule and anti-stereoselectivity.
Asymmetric Aldol Reactions Draw the major organic product(s) formed from the following reaction. | Homework.Study.com The organic product formed in given reaction is shown below. Figure 1. The above reaction takes place between a brominated compound and Li 2 CO 3, LiBr in the presence of DMF that results in the formation of an alkene as the desired product.