Your spinal cord is the long, cylindrical structure that connects your brain and lower back. It contains tissues, fluids and nerve cells. A bony column of vertebrae surrounds and protects your spinal cord. Your spinal cord helps carry electrical nerve signals throughout your body. These nerve signals help you feel sensations and move your muscles.
Utilizing a Double Epidural Electrical Stimulation Implant For SCI
Figure 12.6.1 12.6. 1: Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. The spinal cord is divided into four regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral. The sacral region has a tapered end called the conus medullaris. The bundle of axons inferior to the conus medullaris is the cauda equina.

Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
most superior boundary of the spinal cord. foramen magnum. 2. meningeal extension beyond the spinal cord terminus. filum terminale. 3. spinal cord terminus. conus medullaris. 4. … in the spinal cord the outer layer is the white matter and the inner layer is the grey matter. but in the cerebrum white matter is the inner layer and grey matter

Source Image: baptisthealth.com
Download Image
Brachial Plexus Injury | Living With Paralysis | Reeve Foundation
The spinal cord is a single structure, whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. A person’s conscious experiences are based on neural activity in the brain. The regulation of homeostasis is governed by a specialized region in the brain.

Source Image: washingtoninjury.com
Download Image
Most Superior Boundary Of The Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a single structure, whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. A person’s conscious experiences are based on neural activity in the brain. The regulation of homeostasis is governed by a specialized region in the brain.
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS), which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS, i.e., the dura mater, arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. In most adult mammals it occupies only the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal as the growth of the bones composing the vertebral
Part of Spine That is Most Commonly Injured – Washingtoninjury.com
Nov 3, 2023Anatomy. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS). It is situated inside the vertebral canal of the vertebral column. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. The spinal cord finishes growing at the age of 4, while the vertebral column finishes growing at age 14-18.
Anatomy clinical correlates: Spinal cord pathways | Osmosis

Source Image: osmosis.org
Download Image
What Is a Spine Surgeon?
Nov 3, 2023Anatomy. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS). It is situated inside the vertebral canal of the vertebral column. During development, there’s a disproportion between spinal cord growth and vertebral column growth. The spinal cord finishes growing at the age of 4, while the vertebral column finishes growing at age 14-18.
Source Image: orthoinfo.aaos.org
Download Image
Utilizing a Double Epidural Electrical Stimulation Implant For SCI
most superior boundary of the spinal cord. foramen magnum. 2. meningeal extension beyond the spinal cord terminus. filum terminale. 3. spinal cord terminus. conus medullaris. 4. … in the spinal cord the outer layer is the white matter and the inner layer is the grey matter. but in the cerebrum white matter is the inner layer and grey matter
Source Image: veritaneuro.com
Download Image
Brachial Plexus Injury | Living With Paralysis | Reeve Foundation
Your spinal cord is the long, cylindrical structure that connects your brain and lower back. It contains tissues, fluids and nerve cells. A bony column of vertebrae surrounds and protects your spinal cord. Your spinal cord helps carry electrical nerve signals throughout your body. These nerve signals help you feel sensations and move your muscles.

Source Image: christopherreeve.org
Download Image
Anatomy of the Spine | Wake Spine & Pain Specialists
most superior boundary of the spinal cord c 2. meningeal extension beyond the spinal cord terminus b 3. spinal cord terminus a 4. collection of spinal nerves traveling in the vertebral canal below the terminus of the spinal cord 2. Match the key letters on the diagram with the following terms. a 1. central canal j 2. dorsal horn k 3. dorsal
Source Image: wakespine.com
Download Image
Corticospinal Tract – Physiopedia
The spinal cord is a single structure, whereas the adult brain is described in terms of four major regions: the cerebrum, the diencephalon, the brain stem, and the cerebellum. A person’s conscious experiences are based on neural activity in the brain. The regulation of homeostasis is governed by a specialized region in the brain.
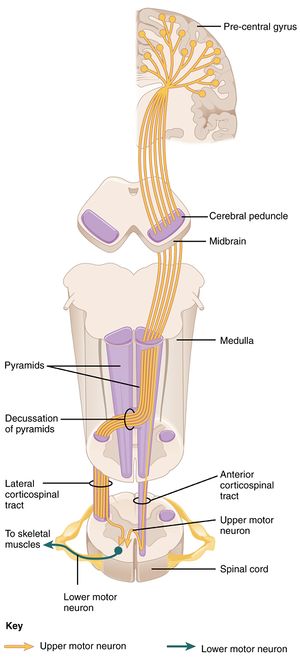
Source Image: physio-pedia.com
Download Image
Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury: Functions Affected & Recovery
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system (CNS), which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. It is covered by the three membranes of the CNS, i.e., the dura mater, arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. In most adult mammals it occupies only the upper two-thirds of the vertebral canal as the growth of the bones composing the vertebral
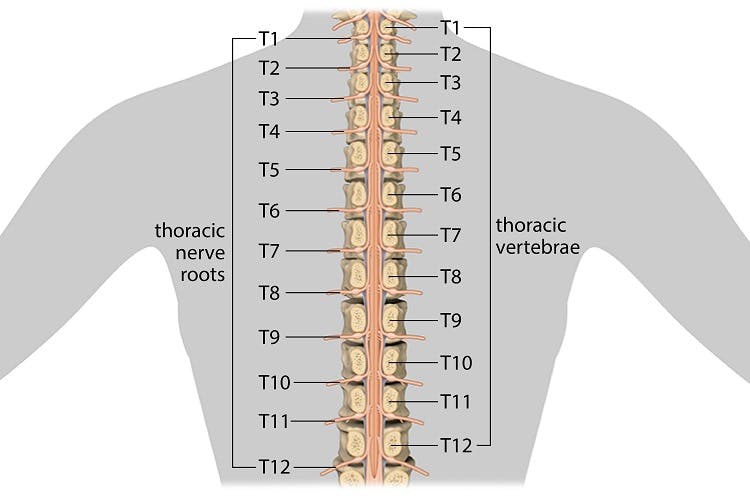
Source Image: flintrehab.com
Download Image
What Is a Spine Surgeon?
Thoracic Spinal Cord Injury: Functions Affected & Recovery
Figure 12.6.1 12.6. 1: Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord. The spinal cord is divided into four regions: cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral. The sacral region has a tapered end called the conus medullaris. The bundle of axons inferior to the conus medullaris is the cauda equina.
Brachial Plexus Injury | Living With Paralysis | Reeve Foundation Corticospinal Tract – Physiopedia
most superior boundary of the spinal cord c 2. meningeal extension beyond the spinal cord terminus b 3. spinal cord terminus a 4. collection of spinal nerves traveling in the vertebral canal below the terminus of the spinal cord 2. Match the key letters on the diagram with the following terms. a 1. central canal j 2. dorsal horn k 3. dorsal