Jul 12, 2023Figure 27.1.3 27.1. 3: Elimination Reactions.These are the reverse of addiion reactions. This reaction results in the forming of a new C-C double bond (π bond) and breaking two single bonds to carbon (in these cases, one of them is H and the other is a halide such as Cl or Br).
The study of Carbon and its compounds – ppt video online download
What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? OH CH3 Le corps H R + CH3 – CH2 – CH – CH3 CH3 -CH2-C-O-CH-CH2 – CH3 + H20 A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them.
Source Image: coursehero.com
Download Image
Nov 17, 2023VIDEO ANSWER: Here is the missing structure of the product of the following reaction. So it’s a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acidic catalyst, and it forms water. So it’s a reaction of Fischer esterification.
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Organic Chemistry Practice Problems-Chemistry Steps
Fill in the missing component in the following reactions. Provide the missing reagents for the reaction below-mentioned. Give the organic product of the given reaction or sequence of reactions: Find the major organic product of the following reaction. Complete the following synthesis by filling in the missing reagents.

Source Image: pubs.acs.org
Download Image
What Is The Missing Reactant In This Organic Reaction
Fill in the missing component in the following reactions. Provide the missing reagents for the reaction below-mentioned. Give the organic product of the given reaction or sequence of reactions: Find the major organic product of the following reaction. Complete the following synthesis by filling in the missing reagents.
It’s taken a long time – late April through early May was hectic – but today I’m thrilled to finally announce the launch of the ” Organic Chemistry Reagent Guide “, a guide designed especially for undergraduate students taking Org1/Org 2. It’s has pretty much all the reagents you need to know about, from Ag2O to Zn (Hg).
Elucidation of Catalytic Propane Dehydrogenation Using Theoretical and Experimental Approaches: Advances and Outlook | Energy & Fuels
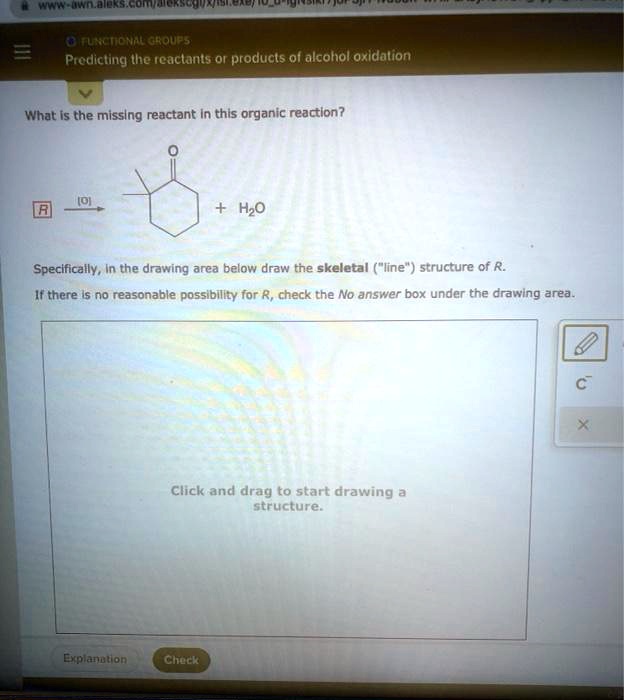
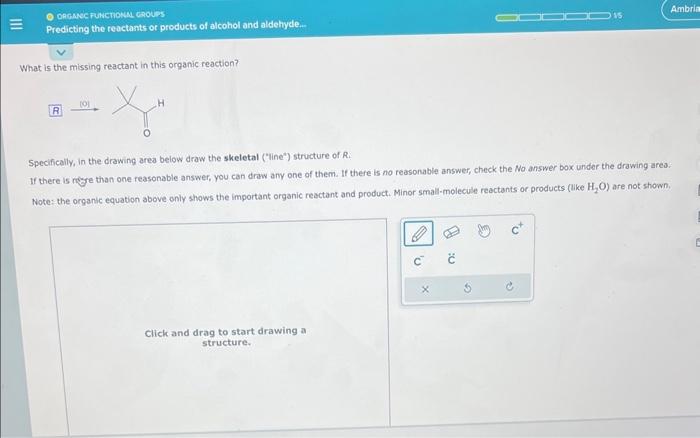
This reactant undergoes a reaction and forms a product, which is a compound with a triple bond between carbon atoms. To determine the missing reactant, we need to think about what type of reaction could convert a double bond into a triple bond. One possible reaction is an addition reaction, where a molecule adds across the double bond.
Typical Acid-Base Exam and Homework Questions — Organic Chemistry Tutor
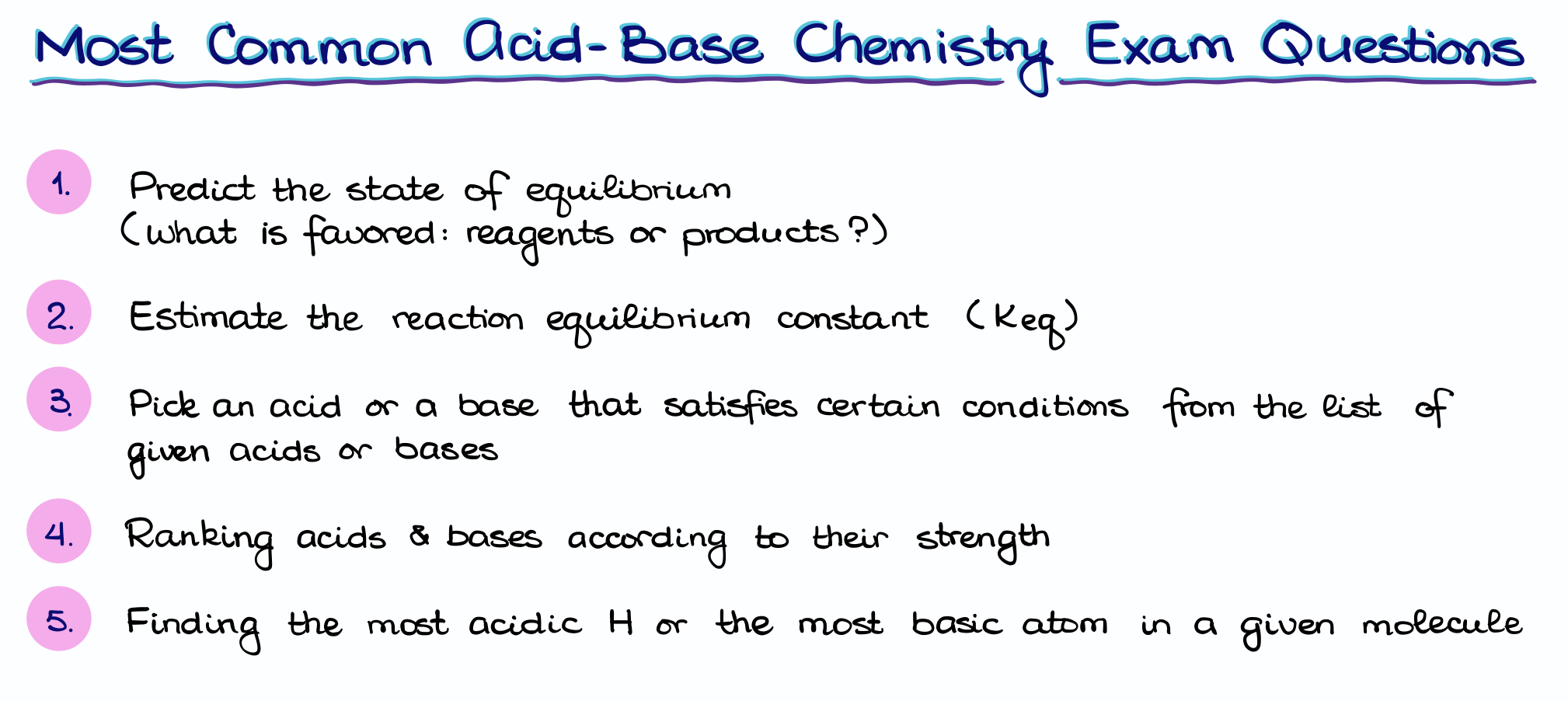
Source Image: organicchemistrytutor.com
Download Image
Solved What is the missing reactant in this organic | Chegg.com
This reactant undergoes a reaction and forms a product, which is a compound with a triple bond between carbon atoms. To determine the missing reactant, we need to think about what type of reaction could convert a double bond into a triple bond. One possible reaction is an addition reaction, where a molecule adds across the double bond.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
The study of Carbon and its compounds – ppt video online download
Nov 17, 2023VIDEO ANSWER: Here is the missing structure of the product of the following reaction. So it’s a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol in the presence of an acidic catalyst, and it forms water. So it’s a reaction of Fischer esterification.

Source Image: slideplayer.com
Download Image
Organic Chemistry Practice Problems-Chemistry Steps
Jul 12, 2023Figure 27.1.3 27.1. 3: Elimination Reactions.These are the reverse of addiion reactions. This reaction results in the forming of a new C-C double bond (π bond) and breaking two single bonds to carbon (in these cases, one of them is H and the other is a halide such as Cl or Br).

Source Image: chemistrysteps.com
Download Image
Solved What is the missing reactant in this organic | Chegg.com
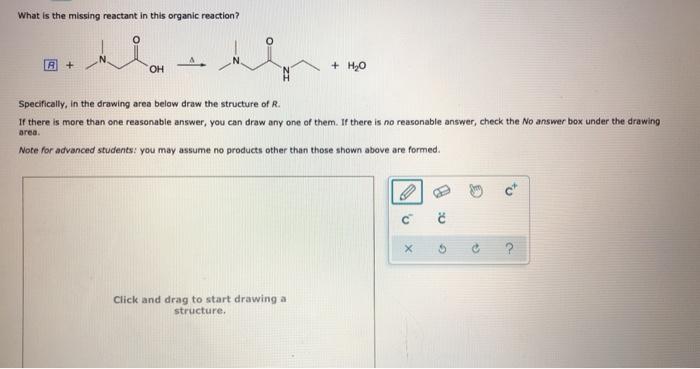
Exercise 6.2.2. Draw electron movement arrows to illustrate the mechanism of the reverse of the reaction in Exercise 6.2.1 : the acid-base reaction between acetate ion ( CH3CO−2 CH 3 CO 2 −, acting as a base) and ammonium ( NH+4 NH 4 + ), acting as an acid). Again, draw out the Lewis structures of reactants and products, including all lone
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4) As A Reagent In Organic Chemistry
Fill in the missing component in the following reactions. Provide the missing reagents for the reaction below-mentioned. Give the organic product of the given reaction or sequence of reactions: Find the major organic product of the following reaction. Complete the following synthesis by filling in the missing reagents.
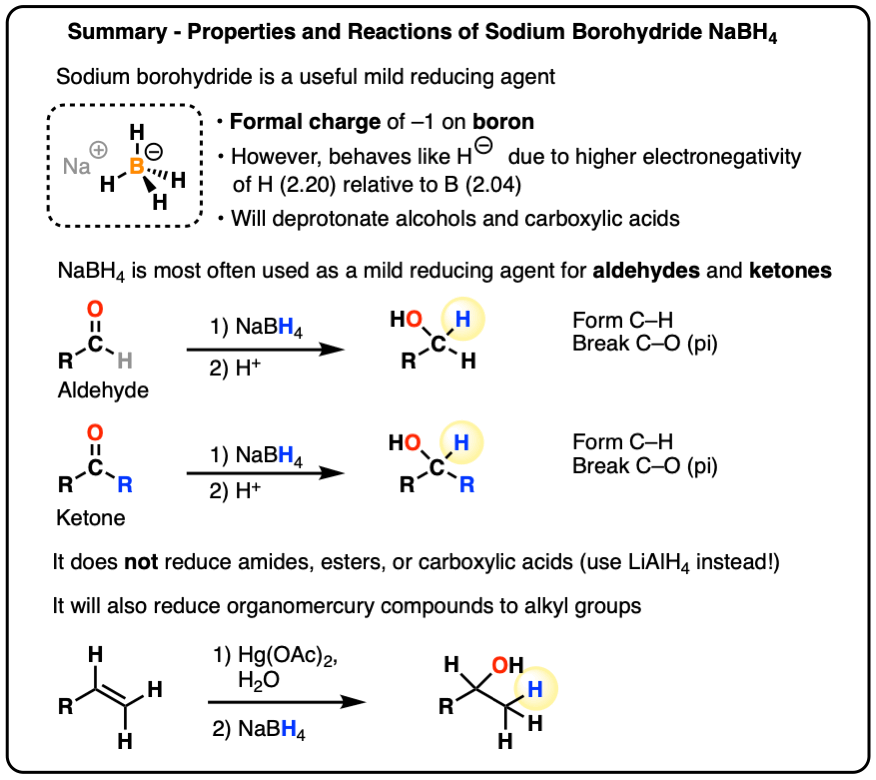
Source Image: masterorganicchemistry.com
Download Image
SOLVED: What is the condensed structure of R? Predicting the reactants or products of esterification What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? CH3 R + CH3-C-OH CH3-C-O-CH-CH3 + HO Specifically,
It’s taken a long time – late April through early May was hectic – but today I’m thrilled to finally announce the launch of the ” Organic Chemistry Reagent Guide “, a guide designed especially for undergraduate students taking Org1/Org 2. It’s has pretty much all the reagents you need to know about, from Ag2O to Zn (Hg).
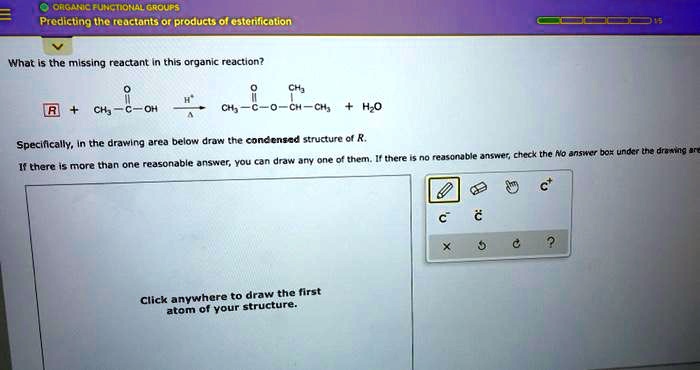
Source Image: numerade.com
Download Image
Solved What is the missing reactant in this organic | Chegg.com
SOLVED: What is the condensed structure of R? Predicting the reactants or products of esterification What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? CH3 R + CH3-C-OH CH3-C-O-CH-CH3 + HO Specifically,
What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? OH CH3 Le corps H R + CH3 – CH2 – CH – CH3 CH3 -CH2-C-O-CH-CH2 – CH3 + H20 A Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the condensed structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them.
Organic Chemistry Practice Problems-Chemistry Steps Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4) As A Reagent In Organic Chemistry
Exercise 6.2.2. Draw electron movement arrows to illustrate the mechanism of the reverse of the reaction in Exercise 6.2.1 : the acid-base reaction between acetate ion ( CH3CO−2 CH 3 CO 2 −, acting as a base) and ammonium ( NH+4 NH 4 + ), acting as an acid). Again, draw out the Lewis structures of reactants and products, including all lone